
Advertisement
In some cases, a lack of appetite may indicate that something is wrong.
There are many possible causes of anorexia nervosa, including illness, drug side effects, and mental health issues such as depression.
Your doctor can test you to identify what's causing the issue and provide you with treatment if your appetite does not go away after several weeks.
1. Irritable bowel syndrome
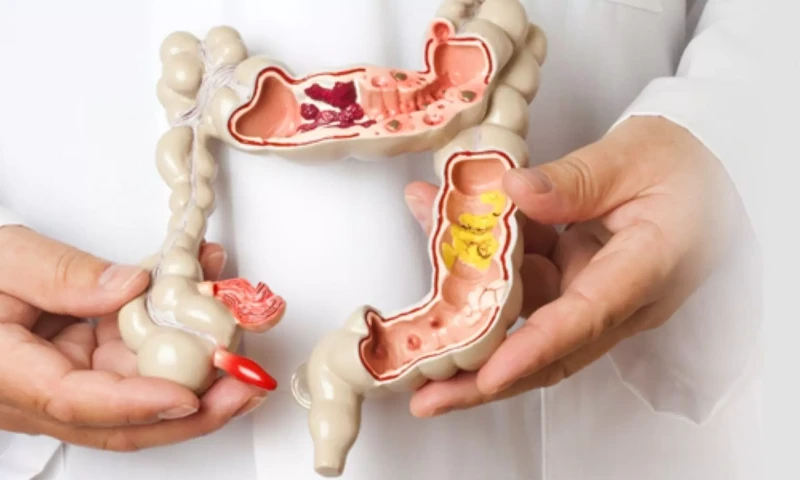
Symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea or constipation that you can't seem to identify may be caused by Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).
When feeling uncomfortable, people with IBS often experience nausea as a reaction.
It is often found that irritable bowel syndrome is related to stress, anxiety, and depression. Stress reduction, regular exercise, and quitting smoking can all help alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome.
2. Heartburn
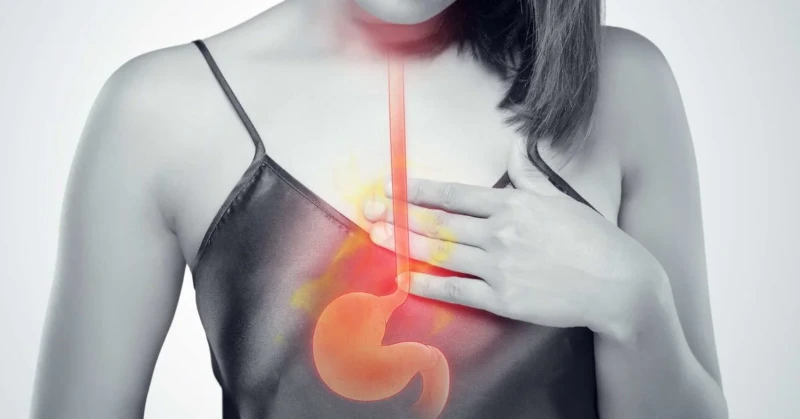
It usually occurs after eating, but can happen at any time. Heartburn is caused by stomach acid coming back up into the esophagus.
People can manage heartburn on their own with lifestyle changes and nonprescription medications like antacids, but it is unfortunately a common symptom. Consult your doctor if the condition becomes frequent or interferes with daily activities.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause heartburn. Treatment may include dietary changes and/or prescription medications. Surgery may also be necessary in extreme cases.
3. Morning sickness
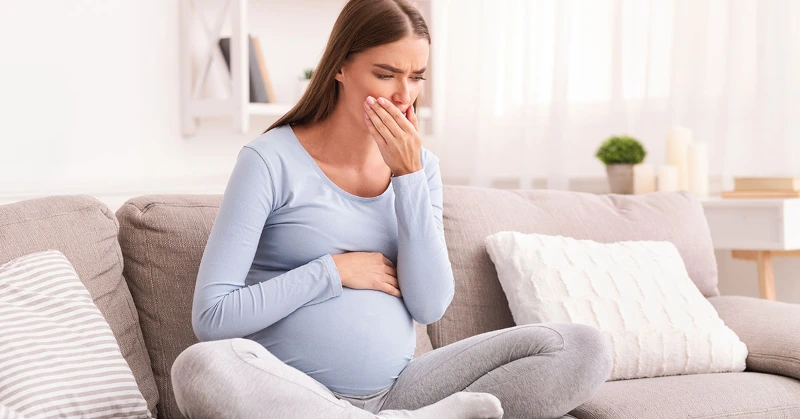

The first trimester of pregnancy is often characterized by nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite for many women. While this is an unfortunate side effect, it can also be managed.
For most women, nausea starts around week 6 and peaks between weeks 8-11 before dissipating by the end of the first trimester; however, some may experience it longer.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is typically responsible for causing preeclampsia, but there are steps you can take to alleviate the symptoms.
Morning sickness can be eased by taking prenatal vitamins, eating smaller meals, and keeping a snack nearby. Antinausea medications such as antihistamines and diuretics may also help.
4. Infections
Once bacteria enter your body through a cut or burn, they multiply and can cause an infection that can progress to sepsis.
Antibiotics, which destroy or prevent bacteria from multiplying, may be prescribed by your doctor depending on the bacteria responsible for your infection.
In addition to adhering to cells and producing toxic substances that weaken our bodies' defenses, bacteria can even resist drugs and antibodies that our immune system produces.
Symptoms like fever, diarrhea, vomiting, fatigue, and aches can be caused by their large size and structure, which can have detrimental effects on the human body.









